Comprehensive Asset Management Planning and Its Application to a CIP
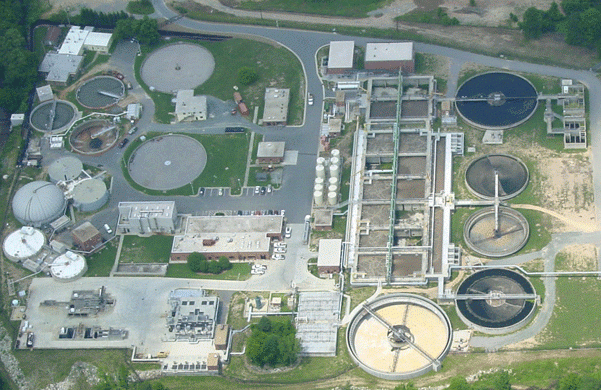
The asset management processes, practices, and tools developed in this pilot project for Goleta Sanitary District (CA) were expanded to include the entire wastewater treatment plant and fleet vehicles and then applied to optimize O&M strategies, prioritize short-term R&R, and project long-range funding needs.
Project Outcomes and Benefits
- Established asset hierarchy, determined consequence of failure (COF), and created an intuitive map to visualize the business risk exposure (BRE) of each major process component.
- Enabled the client to easily visualize data on customized dashboards or drill down into the asset register.
- Conducted condition assessment and data review to determine likelihood of failure (LOF) for 2,300 assets at the WWTP.
- Integrated all risk assessment data into Goleta Sanitary District’s CMMS and developed a Microsoft Power BI decision support tool to continuously monitor asset portfolio performance over time.
- Identification of projects from the asset management business case evaluation priority list that can be designed and bid within the 10-year timeframe of a District CIP.
- Development of a dashboard to allow District staff to easily navigate between the AMP and CIP.

Sean Pour has a wide range of experience helping clients be more proactive in planning, rehabilitation, and replacement activities.


Hazen took a phased data-driven approach to developing an Asset Management Plan (AMP) for Goleta Sanitary District. The project included educating staff on asset management through implementation of a pilot project, developing the District’s asset register hierarchy, populating the asset register, conducting condition assessment and data review, and prioritizing long term investment needs for all assets.
Like many water and wastewater agencies, the district used its Geographic Information System (GIS) as the repository of data for its collection system assets, but lacked a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) or other system to centralize data for its facility assets. To address these challenges, a phased data-driven approach was developed and a proof of concept pilot project was initiated. The wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) influent pump station was selected for the four-month trial because it included the appropriate range of mechanical, electrical, and structural assets for producing a scalable program that could be expanded to the entire plant.

Goleta asset management dashboard.
Although the project included such traditional elements of asset management as data collection, an asset register, and condition assessment, at its core was a set of customized analyses designed to inspire higher confidence in the timing and cost of asset failures and provide a tool for continuously updating asset management calculations as new data becomes available. A computerized asset management model was developed to streamline asset management calculations and visually summarize key operational and financial information in dynamic dashboards that allows the district to review data at a high level as well as "drill down" to source data.

We are now building upon the asset management framework developed for the wastewater treatment plant to improve risk management, minimize life-cycle costs, and better project long-range rehabilitation and replacement funding requirements for the collection system. Hazen will also work with District staff to identify and combine projects from the asset management business case evaluation priority list into large packages that can be designed and bid within the 10-year timeframe of a District CIP and to develop a Dashboard to allow District staff to easily navigate between the AMP and CIP.